What is Data Archiving and Why is it Important?

What is an organisation without its data? No matter how established your business is, if your data is compromised, lost and/or stolen, your company can face costly consequences.
Whether you have an in-house IT team or you’re working with a business IT support company (we hope you’re not leaving your IT to run itself!) that ensures optimal data archiving, we want to bring to your attention a topic that is often misunderstood.
In this article, we’re going to outline the difference between data backup vs data archiving, why data archival is important and how the correct implementation will help you minimise risks.
What is the difference between backup and archive?
When it comes to data, backups and archiving serve different purposes. Understanding the basics of each and the difference between them is essential to protecting your data.
However, because these terms are sometimes (wrongfully) used interchangeably, it can make it difficult for enterprises to ensure that the backup and archive data methodology they use is right.
As a fundamental difference, data backup is generally for short-term archiving and recovery, while archives are for long-term archival data storage, retention and space management.
What is data backup?
Data backup is necessary for disaster recovery and is defined as making copies of your files – so you can retrieve the data in case of an unexpected event. That can be critical disruptions to your hardware or software (cyberattacks, natural disasters) and proper data backups will ensure business continuity.
What is data archiving?
Data archiving or data storage is defined as the process of moving data to another location and storing it for long periods of time. The purpose of this is to make sure that you retain important records and can access them years after they’ve been created.
Is the archive a backup?
As opposed to backup, archive data is not just a copy, but the inactive data an enterprise has to keep. The archiving process relocates the data to a less expensive storage location.
Types of data storage mediums: data storage devices such as USB flash drives and optical media storage (DVDs, CDs, BDs), cloud storage and cloud backup.
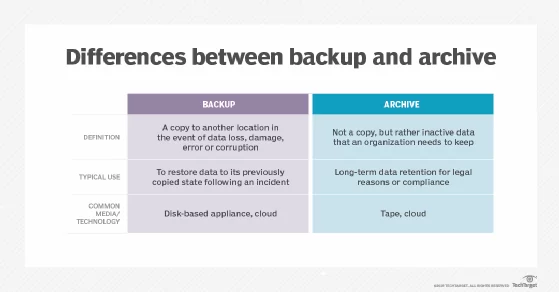
Data backup vs archiving. Source: TechTarget
Why archive data
One of the purposes of data archiving is legal compliance requirements. When it comes to data storage laws in Australia, businesses need to comply with specific data retention regulations. The specific data archiving requirements depend on the industry or size of your organisation.
For example, some required data storage examples would be transaction records for a bank or patient records for a general practitioner.
Other advantages of archiving data include reduced storage costs, retaining historical data, increased capacity and systems running more efficiently.
Why data archiving is important
Besides the legal requirements of each organisation, data archiving can help your organisation in ways that you might not have anticipated. Here are 3 issues data archiving can help you avoid:
- Losing sight of your purpose. Archival data is an invaluable way to help retain the story of your business and help bring the mission back to the centre if you feel like you’ve lost sight of your mission.
- You need to access specific information. Data archiving solves your problem when you need to quickly find a document – for example, for legal matters.
- A liability. Not knowing (or having easy access to) what’s in your company’s past means that you are unable to be prepared for what could resurface.
What are the benefits of data archiving?
Data archiving solutions centre around 5 main key benefits: reduced cost, increased performance, data loss prevention, increased security and compliance.
According to research, when archiving company data, costs can be reduced by up to 50 per cent.
In general, companies store around 100 terabytes of data. Data archiving is cheaper than just backing it up, so that means significant changes for each terabyte. That reduces backup costs and also avoids building costs.
4 data archiving best practices
Here are the 5 best practices to consider for creating a successful data archiving strategy
- Sort data. Before archiving, it’s important to identify your data and categorise it. What’s ready to archive and what’s still needed now? Also, some digital information might not be relevant to keep long-term. So part of your strategy should be thorough categorisation.
- Plan for compliance. As mentioned above, planning for regulatory compliance is essential for the lawful functioning of your business. So you need to take into account the stringency of the requirements to create the best strategy for your enterprise.
- Select the right archiving tool. There are a lot of archiving tools available, each with different pricing and solutions. You should choose depending on the type of business and whether you simply need the software for data archiving or you want a more complex solution.
- Create a data archiving policy. This policy will help your organisation keep track of all the structures and processes that can help with planning how long you should retain data.
Creating a strong data archiving strategy
We hope that we made you aware that a successful data archiving strategy will help your organisation stay compliant, save money and minimise security risks. Each business is different and, as your managed service provider, we can provide a tailored data archiving solution to ensure that your enterprise is running smoothly. Contact us today for a free audit.
